- Home
- /
- Blog
Expansion Joint What Is
Expansion Joint What Is
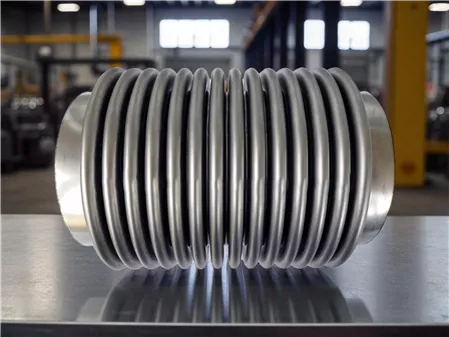
What is an Expansion Joint (Compensator)?
An expansion joint (compensator) is a flexible connection element used to absorb expansion, contraction, vibration, or movement in piping systems.
Brief Definition
It balances expansion and movement in pipelines caused by temperature changes, pressure, seismic activity, or mechanical vibrations, ensuring safe operation.
Where Is It Used?
- Heating and cooling systems
- Steam and hot water pipelines
- HVAC systems
- Refineries and power plants
- Shipbuilding and marine machinery
- Industrial piping systems
What Does It Do?
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Handles thermal expansion | Absorbs expansion/contraction in pipes |
| Dampens vibration | Reduces transmission from pumps or equipment |
| Reduces noise | Minimizes sound propagation in pipelines |
| Allows displacement | Tolerates movement from ground shifts or settlements |
Types of Expansion Joints
| Type | Feature | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Metal Expansion Joint | Resistant to high temperature and pressure | Steam, hot water lines |
| Rubber Expansion Joint | Flexible, provides vibration and sound isolation | Pump connections |
| PTFE (Teflon) Expansion Joint | Chemical-resistant | Acid and chemical pipelines |
| Fabric (Canvas) Expansion Joint | Lightweight and flexible | HVAC ducts |
Why Is It Important?
- Pipes may crack or burst
- Flange connections may loosen
- System lifetime decreases
- Safety risks increase
Usage Example
In a steam pipeline, a 100°C temperature rise can cause a 20-meter pipe to expand by about 30 mm. Without a compensator, this expansion can lead to serious damage to the system.
Join Our Newsletter
Be informed about innovations about us



